Cellulitis Risk Calculator
Assess Your Cellulitis Risk
Complete this 30-second risk assessment based on your health factors. Understanding your risk helps you take appropriate precautions to prevent serious infection.
Risk Assessment Guide
This tool helps you understand your individual risk factors for developing cellulitis from a minor abrasion. Based on your answers, you'll receive a personalized risk level and recommendations.
Why your risk matters: Early intervention significantly improves outcomes. The risk calculator helps you take appropriate precautions before signs of infection develop.
Key Takeaways
- Abrasion wounds break the skin barrier, letting bacteria invade.
- Common culprits are Staphylococcus aureus and a gram‑positive bacterium that lives on skin and Streptococcus pyogenes. It can cause rapid tissue inflammation.
- Early signs of infection include redness spreading beyond the wound, warmth, swelling and fever.
- Proper wound cleaning, keeping the area moist, and monitoring for changes dramatically reduce risk.
- If you notice cellulitis signs, seek medical care promptly to start antibiotics.
Every year in the UK, more than 200,000 people are treated for cellulitis after what started as a simple scrape. Most of those cases could have been avoided with a few minutes of proper care. Let’s break down why an everyday abrasion can turn into a serious skin infection and what you can do to stop it.
What Is an Abrasion?
Abrasion is a superficial wound that scrapes off the top layers of skin, typically the epidermis and sometimes part of the dermis. It results from friction, a fall, or a sharp object sliding across the skin. Because the protective barrier is broken, the wound becomes a gateway for microbes that normally live harmlessly on the surface.
Understanding Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a deep bacterial infection of the skin and underlying soft tissue. It is characterized by expanding redness, swelling, heat, and pain, often accompanied by fever. The condition can progress quickly, sometimes leading to complications such as abscesses or sepsis if untreated.
How an Abrasion Turns Into Cellulitis
The skin’s outermost layer, the skin barrier, acts like a wall that keeps microbes out. When an abrasion tears this wall, bacteria can slip beneath the surface and meet the immune system, which then mounts an inflammatory response. If the immune response can’t clear the invaders fast enough, they multiply, release toxins, and trigger the classic signs of cellulitis.
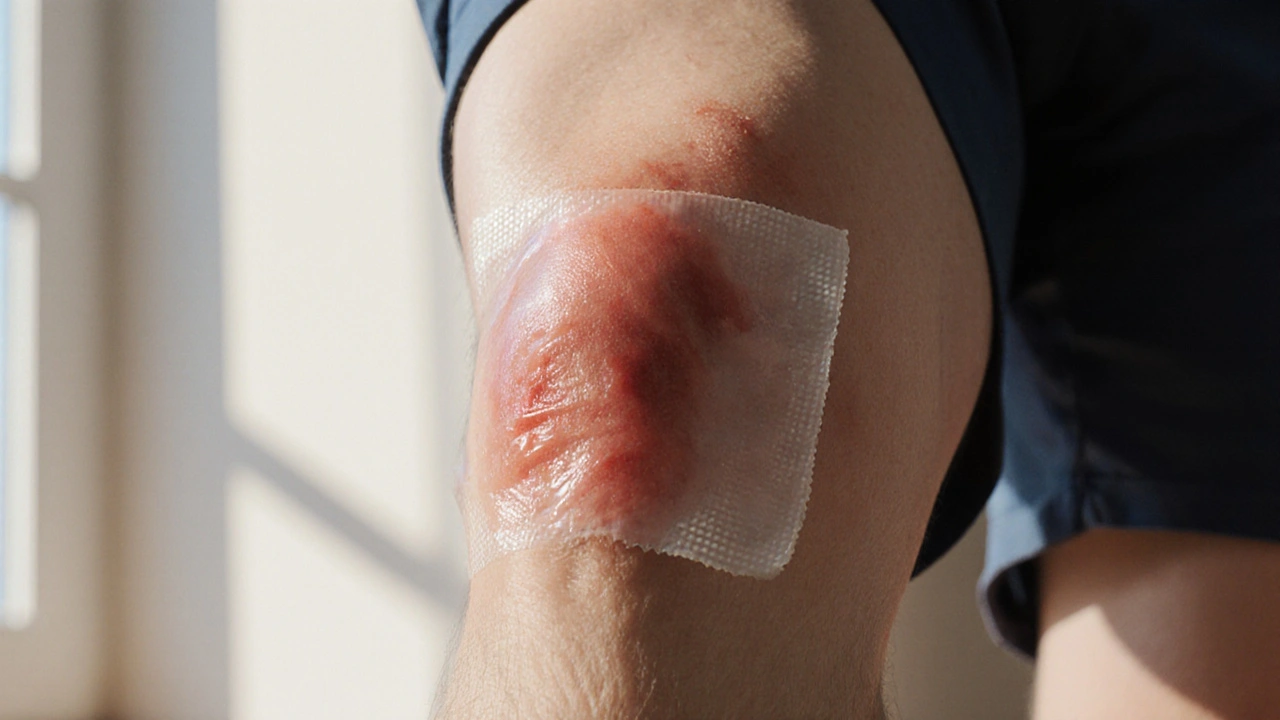
Typical Bacterial Invaders
| Organism | Gram Stain | Typical Source | Key Virulence Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | Positive | Normal skin flora | Protein A, toxins |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Positive | Throat, skin carriers | M protein, streptolysins |
| Gram‑negative rods (e.g., Pseudomonas) | Negative | Contaminated water, soil | Exotoxins, biofilm |
Risk Factors That Raise the Infection Odds
- Diabetes or peripheral vascular disease - reduced blood flow hampers healing.
- Immunocompromised state - chemotherapy, steroids, HIV.
- Chronic skin conditions - eczema, psoriasis, athlete’s foot.
- Previous episodes of cellulitis - scar tissue creates weak spots.
- Heavy alcohol use - weakens immune defenses.
Early Warning Signs: Is Your Abrasion Getting Infected?
Not every scrape turns nasty, but watch for these red flags within 48‑72hours:
- Redness spreading outward more than 2cm from the wound.
- Increasing pain or tenderness, especially when touched.
- Warmth or a feeling of heat around the area.
- Swelling that makes the skin feel tight.
- Fever, chills, or feeling generally unwell.
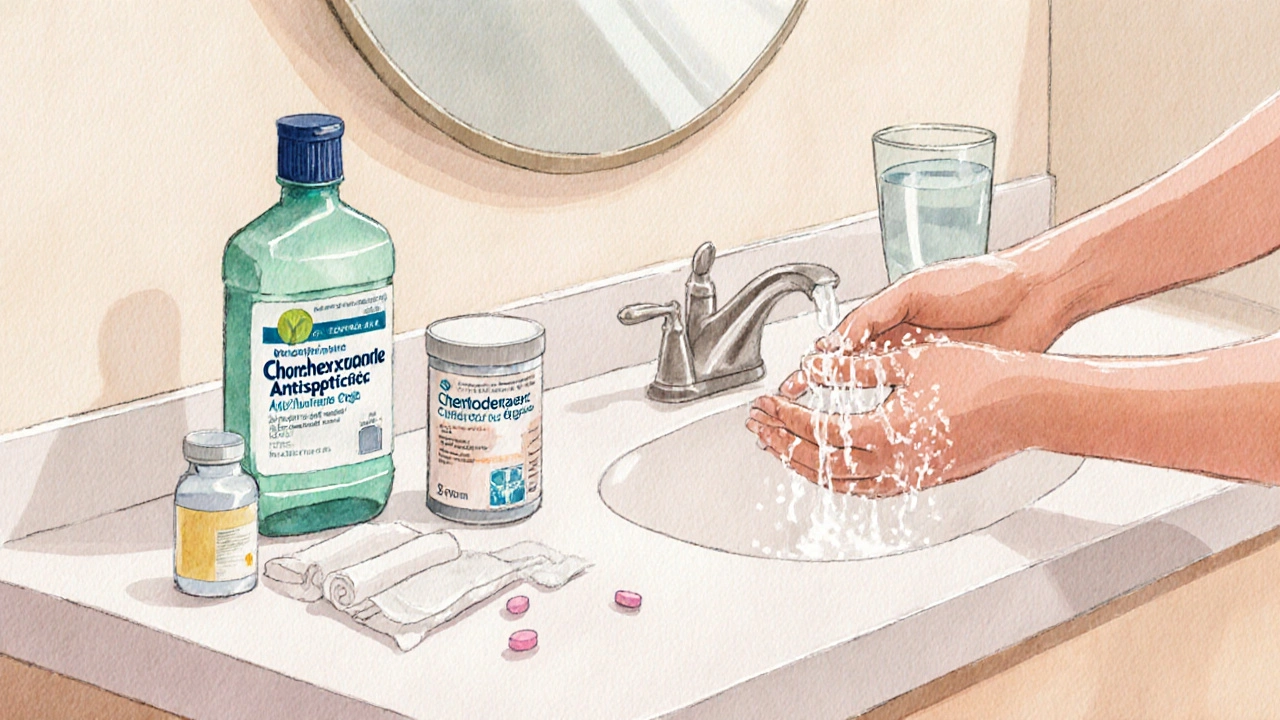
Step‑by‑Step Wound‑Care Checklist
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Rinse the abrasion under cool running water to remove debris.
- Gently clean with a mild antiseptic solution (e.g., chlorhexidine).
- Pat dry with a clean gauze - avoid rubbing.
- Apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment (bacitracin or mupirocin).
- Cover with a non‑adhesive sterile dressing; change daily or if it becomes wet.
- Monitor the wound daily for the warning signs listed above.
What Happens If Cellulitis Develops?
Once bacterial infection reaches the deeper layers, oral antibiotics become the mainstay of treatment. Common first‑line choices include dicloxacillin, cephalexin, or clindamycin, depending on local resistance patterns. Severe cases may need intravenous therapy in a hospital setting.
Typical course of therapy lasts 7‑10days, but it’s crucial to finish the full prescription even if symptoms improve early. Stopping too soon can let surviving bacteria rebound, leading to recurrence.
When to Call a Doctor
- Rapidly spreading redness or swelling.
- Fever above 38°C (100.4°F) or chills.
- Pain that worsens despite dressing changes.
- Redness involving the face, hands, or genitals - these areas can develop complications quickly.
- Any sign of an abscess (fluctuant, pus‑filled lump).
Quick Reference: Abrasion vs. Cellulitis
| Feature | Abrasion | Cellulitis |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Surface (epidermis) | Deeper skin layers & subcutaneous tissue |
| Redness | Localized, sharp edges | Diffuse, spreading beyond wound margin |
| Pain | Sharp, worsens with pressure | Throbbing, constant, may radiate |
| Heat | Usually absent | Warm to touch |
| Systemic symptoms | None | Fever, chills, malaise |
Bottom Line
Scrapes are common, but they don’t have to become emergencies. By treating an abrasion like a tiny doorway-cleaning it, sealing it, and watching for signs-you give your immune system the best chance to keep bacteria at bay.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use honey to treat an abrasion?
Medical‑grade honey has antibacterial properties and can be helpful on clean, minor wounds, but it should be used under guidance. For most everyday scrapes, a standard antiseptic ointment is sufficient and easier to manage.
How long does cellulitis usually take to heal?
With appropriate antibiotics, symptoms often improve within 48‑72hours, and the skin usually clears up in 1‑2weeks. Completing the full course is essential to prevent relapse.
Is it safe to swim with an abrasion?
Swimming exposes the wound to water‑borne microbes and can delay healing. Keep the abrasion covered and avoid pools, hot tubs, or natural bodies of water until it has fully closed.
Why does cellulitis feel hot?
The infection triggers inflammation, which increases blood flow to the area. More blood means more heat, creating that characteristic warm sensation.
Can antibiotics cause side effects?
Yes, common side effects include stomach upset, rash, or diarrhea. Rarely, antibiotics can affect gut flora, leading to yeast infections. If you notice severe reactions, contact a healthcare professional.


Shana Shapiro '19
October 13, 2025 AT 13:24Reading through this guide felt like watching a small drama unfold-first the innocent scrape, then the looming threat of infection. It’s heartbreaking how quickly a simple abrasion can become a serious health issue. I’m reminded of how the skin is our first line of defense, a fragile barrier we often take for granted. The detailed steps you’ve laid out for wound care are both practical and reassuring. Thank you for highlighting the importance of cleaning, antibiotic ointment, and regular dressing changes. It’s these simple actions that can keep us out of the hospital. Knowing the signs of cellulitis early can truly save lives. Your explanation of why certain bacteria love these broken grounds is clear and compassionate. I especially appreciate the emphasis on monitoring for fever and swelling. It’s a solid reminder that we all need to be vigilant about our skin health. Please keep sharing such valuable information; it really makes a difference.
Jillian Bell
October 17, 2025 AT 14:37Look, they don’t want us to actually understand how the big pharma machines profit from our scrapes. Every tiny wound is a gateway for a hidden agenda, and the “simple” steps they list are just a distraction from the fact that we’re being monitored for infection patterns. You think you’re protecting yourself with a bandage, but you’re feeding the data farms that decide who gets antibiotics and who gets left to suffer.
Lindsey Bollig
October 21, 2025 AT 15:51Alright, let’s break this down step by step so you can feel confident handling any little scrape that comes your way.
First, always start with clean hands-nothing beats soap and water to keep your own germs from joining the party.
Next, rinse the abrasion under cool running water for at least 30 seconds; this flushes out dust, dirt, and any unwanted microbes.
If you have a mild antiseptic like chlorhexidine, dab it gently-no need to scrub aggressively, just enough to coat the wound.
After that, pat the area dry with a clean gauze; rubbing can tear fragile tissue and cause more bleeding.
Now comes the ointment-apply a thin layer of bacitracin or mupirocin; this creates a barrier that’s hostile to bacteria while keeping the wound moist, which actually speeds healing.
Cover it with a non‑adhesive sterile dressing; change it daily or sooner if it gets wet or dirty-this helps you keep an eye on the wound’s progress.
Check the surrounding skin each day for any spreading redness beyond two centimeters, increasing warmth, or swelling that feels tight.
Look out for systemic signs like fever over 38°C, chills, or a general feeling of being lousy-these are red flags for cellulitis and need prompt medical attention.
If you notice any of those signs, call your doctor within 24 hours; early antibiotics can prevent a nasty infection from getting out of hand.
For people with diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, or compromised immune systems, be extra vigilant-these conditions slow healing and raise infection risk.
In those high‑risk cases, consider seeing a healthcare professional sooner rather than later, even if the wound looks mild.
Remember, keeping the wound moist (not soggy) is key; a dry scab can crack and re‑open, inviting bacteria back in.
Stay hydrated and maintain good nutrition; your body needs protein and vitamins to rebuild skin layers effectively.
Finally, if you’re unsure about any step, don’t hesitate to ask a pharmacist or nurse-they’re happy to walk you through proper wound care.
By following these steps, you dramatically lower the chances of an abrasion turning into cellulitis, keeping you healthy and out of the ER.
Daniel Buchanan
October 25, 2025 AT 17:04Hey folks, just a quick reminder that anyone can help each other out with proper wound care. No matter who you are, washing hands, cleaning the scrape, and covering it properly is something we all can do together. Let’s keep the conversation supportive and share any tips you’ve found useful.
Lena Williams
October 29, 2025 AT 17:17so i was readin about the whole abrasion thing and like wow its crazy how small cuts can become big probz i mean you just think a little scrape is no big deal but then bacteria start throwin a party in there and before u know it you got cellulitis lol also i found out that the size of the wound matters big time like a 2cm scratch is way more risky than a teeny one i guess keep it clean and dont forget the ointment ya know? also i think people should be more chill about checking for redness and swelling cause sometimes i just ignore it till it gets worse. suuuuper important to keep an eye on it daily!
Sierra Bagstad
November 2, 2025 AT 18:31The microbiology outlined here is essentially correct: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are indeed the predominant pathogens in abrasion‑related cellulitis. The virulence factors, such as protein A and M protein, facilitate immune evasion, thereby augmenting the infection’s progression. Early intervention with appropriate antibiotics, as indicated, remains the cornerstone of therapy.
Alan Kogosowski
November 6, 2025 AT 19:44One might argue that the presented risk calculator, while user‑friendly, oversimplifies the multifactorial nature of cellulitis susceptibility. Nevertheless, the inclusion of variables such as diabetes, immunosuppression, and wound size provides a pragmatic framework for laypersons. In practice, however, clinicians often weigh additional factors-namely, the anatomical location of the abrasion, the presence of chronic edema, and the patient's overall nutritional status. Moreover, the dichotomous response options may mask the gradations inherent in clinical presentation. Consider augmenting the questionnaire to capture these nuances, thereby enhancing predictive accuracy.
Ben Lee
November 10, 2025 AT 20:57I totally get that we all want to help each other out, so here’s a friendly reminder to double‑check your wound after the first few days. Sometimes the redness can spread a bit, but if it’s still within a centimeter of the original scrape and there’s no fever, you’re probably fine. Just keep the dressing clean and change it daily, and you’ll be good.
David Brice
November 14, 2025 AT 22:11Listen up, everyone-if you think a little scrape is no big deal, think again. I’m not here to sugarcoat it; you need to treat that wound like it’s a battlefield. Clean it, cover it, and keep an eye out for any sign of infection-redness, swelling, fever. If you’re sloppy, you’ll end up in the ER and that’s on you. Don’t be lazy, be proactive.
Zachary Schroer
November 18, 2025 AT 23:24Honestly, the whole “simple wound care” narrative is just textbook fluff-real life is messier. But sure, let’s all pretend washing hands is the ultimate solution. 🙄🤦♂️
Stacy Whitman
November 23, 2025 AT 00:37They’re taking our health hostage.
Kim and Lin
November 27, 2025 AT 01:51We all need to watch each other's backs with these scrapes, so keep it clean and check for fever-let’s not be strangers to each other's health 😊
Kemari Nielson
December 1, 2025 AT 03:04Proper cleaning and timely monitoring are essential to prevent cellulitis.
Steve Helsel
December 5, 2025 AT 04:17Well, this article does a decent job of covering the basics, though I wish it went a bit deeper into the specifics of antibiotic selection.
Steve Moody
December 9, 2025 AT 05:31Ah, dear readers, let us rejoice in the clarity of this exposition-truly, it is a beacon of knowledge, a masterclass, if you will-where every point is meticulously articulated, and every nuance is painstakingly addressed; indeed, the authors have spared no detail, and I, for one, find myself utterly compelled to applaud such an effort, bravo! 😊
Adrian Hernandez
December 13, 2025 AT 06:44We’re being fed lies about simple scrapes-it’s a distraction while the elite manipulate our immune responses behind the scenes.
Jessie Eerens
December 17, 2025 AT 07:57Consider, if you will, the philosophical implications of a wound; it is not merely a breach of flesh, but a paradox, an invitation to contemplate the fragility of the human condition, the ever‑present tension between decay and regeneration, the silent dialogue between microbes and the host, a microcosm of struggle that mirrors the larger cosmos.
Caroline Lane
December 21, 2025 AT 09:11hey i read thsi and im thinkng t hat we should maybe try not to be so over the top about it, like i get it some people are scared but its not the end of the world if you just wash it.
Geneva Lyra
December 25, 2025 AT 10:24Let’s remember that wound care is universal-different cultures have their own herbal remedies and traditional methods that can complement modern practices. Sharing these diverse approaches can enrich our collective understanding and help everyone stay healthy.